Airtable
Airtable is an easy-to-use online platform for creating and sharing relational databases.
The Airtable Wrapper allows you to read data from your Airtable bases/tables within your Postgres database.
Preparation
Before you can query Airtable, you need to enable the Wrappers extension and store your credentials in Postgres.
Enable Wrappers
Make sure the wrappers extension is installed on your database:
1 | |
Enable the Airtable Wrapper
Enable the airtable_wrapper FDW:
1 2 3 | |
Store your credentials (optional)
By default, Postgres stores FDW credentials inside pg_catalog.pg_foreign_server in plain text. Anyone with access to this table will be able to view these credentials. Wrappers is designed to work with Vault, which provides an additional level of security for storing credentials. We recommend using Vault to store your credentials.
Get your token from Airtable's developer portal.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | |
Connecting to Airtable
We need to provide Postgres with the credentials to connect to Airtable, and any additional options. We can do this using the create server command:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
1 2 3 4 5 | |
Create a schema
We recommend creating a schema to hold all the foreign tables:
1 | |
Entities
The Airtable Wrapper supports data reads from the Airtable API.
Records
The Airtable Wrapper supports data reads from Airtable's Records endpoint (read only).
Operations
| Object | Select | Insert | Update | Delete | Truncate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Records | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Usage
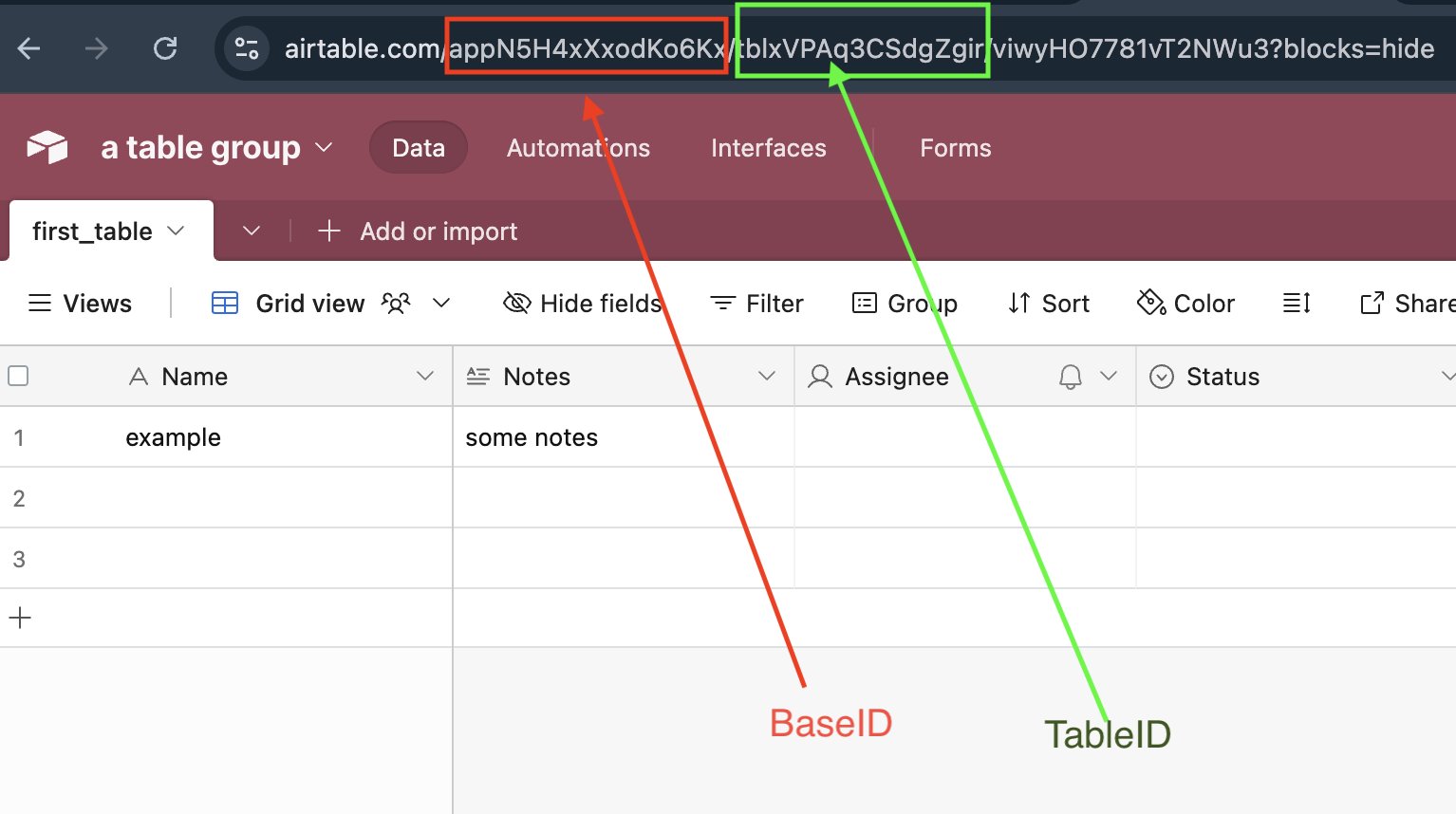
Get your base ID and table ID from your table's URL.
Note
Foreign table names must be lowercase in PostgreSQL, regardless of capitalization in Airtable.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
Notes
- The table requires both
base_idandtable_idoptions - Optional
view_idcan be specified to query a specific view
Supported Data Types
The Airtable Wrapper maps Airtable field types to PostgreSQL data types. Use this reference when defining your foreign table columns.
Text Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single line text | text |
name text |
No length limit in PostgreSQL |
| Long text | text |
description text |
Preserves line breaks |
text |
email text |
Validate in application if needed | |
| URL | text |
website text |
Store as plain text |
| Phone number | text |
phone text |
Preserves formatting |
Numeric Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | numeric, integer, bigint, real, double precision |
quantity integer |
Choose based on precision needs |
| Currency | numeric |
price numeric(19,4) |
Use precision for currency calculations |
| Percent | numeric |
rate numeric(5,4) |
Stored as decimal (e.g., 75% = 0.75) |
| Autonumber | bigint |
row_num bigint |
Auto-generated, read-only |
Selection Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single select | text |
status text |
Returns option name as string |
| Multiple select | jsonb |
tags jsonb |
Returns JSON array of option names |
| Checkbox | boolean |
is_active boolean |
true when checked |
Date/Time Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | date |
due_date date |
ISO 8601 format |
| Created time | timestamp |
created_at timestamp |
Auto-generated by Airtable |
| Last modified time | timestamp |
updated_at timestamp |
Auto-updated by Airtable |
User/Collaborator Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Created by | jsonb |
created_by jsonb |
Contains {id, email, name} |
| Last modified by | jsonb |
modified_by jsonb |
Contains {id, email, name} |
| User | jsonb |
assigned_to jsonb |
Contains user object |
Complex Fields
| Airtable Field Type | PostgreSQL Type | Example | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple record links | jsonb |
related_records jsonb |
Array of linked record IDs |
| Attachments | jsonb |
files jsonb |
Array of attachment objects with url, filename, size |
| Lookup | jsonb |
lookup_values jsonb |
Values from linked records |
| Rollup | Varies | total numeric |
Match to rollup result type |
| Formula | Varies | computed text |
Match to formula result type |
Column Name Mapping
PostgreSQL and Airtable handle column names differently. Understanding these differences is essential for successful data mapping.
Understanding Case Sensitivity
PostgreSQL identifiers are case-insensitive by default and are folded to lowercase. Airtable field names preserve case exactly as entered.
| PostgreSQL Column | Airtable Field | Match? |
|---|---|---|
name |
name |
✅ Yes |
name |
Name |
❌ No - Airtable field is uppercase |
firstname |
FirstName |
❌ No - Case mismatch |
first_name |
First Name |
❌ No - Space in Airtable name |
Using Quoted Column Name
When your Airtable field name doesn't match PostgreSQL's lowercase convention, use double-quotes " to enclose the column name to explicitly map columns:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
Best Practices
- Always check your Airtable field names - Open your Airtable base and note the exact spelling and capitalization
- Use quoted column name liberally - When in doubt, explicitly quote the column name to avoid silent NULL values
- Matching is by name, not position - You can define columns in any order and omit columns you don't need
Working with Array and JSON Fields
Several Airtable field types return JSONB data in PostgreSQL. Here's how to work with them effectively.
Multiple Select Fields
Multiple select fields are returned as JSON arrays of strings.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | |
Linked Records
Linked record fields return JSON arrays of record IDs.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | |
Attachments
Attachment fields return JSON arrays containing file metadata.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | |
User/Collaborator Fields
User fields return JSON objects with user details.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
Query Pushdown Support
This FDW doesn't support query pushdown. All filtering is performed locally in PostgreSQL after fetching data from Airtable.
Performance Consideration
For large Airtable bases, consider using Airtable Views to pre-filter data, or use the optional view_id parameter to limit the records fetched.
Limitations
This section describes important limitations and considerations when using this FDW:
Read-Only Access
The Airtable Wrapper provides read-only access. Write operations are not supported:
- ✅
SELECT- Fully supported - ❌
INSERT- Not supported - ❌
UPDATE- Not supported - ❌
DELETE- Not supported - ❌
TRUNCATE- Not supported
To modify Airtable data, use the Airtable API directly.
Other Limitations
- No query pushdown - All filtering happens locally after data is fetched
- Large datasets - Performance may degrade with large result sets due to full data transfer
- Computed fields - Formula, rollup, and lookup fields work but require matching the output type
- Views - Must be pre-configured in Airtable before referencing
- Block features - Airtable Blocks/Apps are not accessible
- Materialized views - May fail during logical backups; use regular views instead
Troubleshooting
All Columns Return NULL
Symptom: Query returns the correct number of rows, but all column values are NULL.
Cause: Column name mismatch between PostgreSQL and Airtable.
Solution:
-
Check the exact field names in Airtable (including capitalization and spaces)
-
Use quoted column name to map columns correctly:
1 2 3 4 5 | |
"Column Does Not Exist" Error
Symptom: Error message stating a column doesn't exist.
Cause: Case sensitivity mismatch or typo in field name.
Solution: Verify the Airtable field name and use quoted column name:
1 2 | |
Type Conversion Errors
Symptom: Error when querying, mentioning type mismatch.
Cause: PostgreSQL column type doesn't match Airtable field data.
Solution: Refer to the Supported Data Types section and adjust your column type:
1 2 3 | |
Empty Results from JSONB Queries
Symptom: JSONB containment queries (?, @>) return no results.
Cause: Incorrect JSON path or data structure assumption.
Solution: First inspect the raw JSONB structure:
1 2 3 4 | |
Slow Query Performance
Symptom: Queries take a long time to execute.
Cause: No query pushdown means all data is fetched before filtering.
Solution:
-
Create an Airtable View with the filters you need
-
Use
view_idin your foreign table options:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | |
Examples
Basic Table Query
This example creates a foreign table for a simple product catalog:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
Query an Airtable View
Create a foreign table from an Airtable View for pre-filtered data:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | |
Working with Tags (Multiple Select)
Query products by their tags:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | |
Complex Query with User Data
Combine multiple field types in a practical example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | |